Endoscopic Brain Surgery
Endoscopic brain surgery, also known as endoscopic neurosurgery or endonasal endoscopic surgery, is a minimally invasive surgical technique that utilizes an endoscope to access and treat conditions within the brain. This approach allows surgeons to perform procedures through small incisions or natural openings, such as the nostrils, reducing the need for large incisions and minimizing trauma to surrounding tissues. Here are some key points about endoscopic brain surgery:
-
Access through Natural Openings:
- Endoscopic brain surgery often involves accessing the brain through natural openings, such as the nostrils or mouth, rather than creating large incisions in the skull.
-
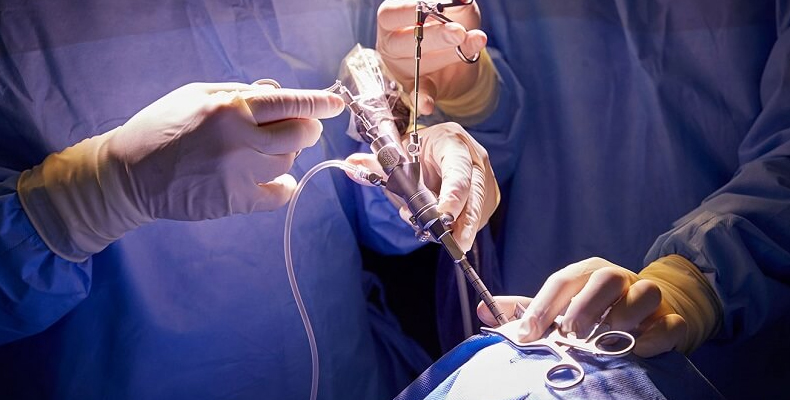
Endoscope Usage:
- An endoscope is a thin, flexible tube with a light and a camera on the end that allows surgeons to visualize the surgical area on a monitor.
- The endoscope is inserted through a small opening, and surgical instruments may be introduced through the same or additional small incisions.
-
Conditions Treated:
- Endoscopic brain surgery is used to treat various conditions, including pituitary tumors, skull base tumors, hydrocephalus, and certain types of cysts or lesions.
- It is particularly well-suited for lesions located in areas that are challenging to reach with traditional open surgery.
-
Minimally Invasive Approach:
- The minimally invasive nature of endoscopic surgery generally leads to reduced postoperative pain, shorter hospital stays, and quicker recovery compared to traditional open surgeries.
-
Pituitary Surgery:
- One common application of endoscopic brain surgery is in pituitary surgery, where tumors or abnormalities in the pituitary gland are accessed and treated through the nasal passages.
-
Collaboration with Other Specialties:
- Endoscopic brain surgery often involves collaboration between neurosurgeons and otolaryngologists (ENT surgeons) to navigate and access the surgical site.
-
Advancements and Technology:
- Advances in endoscopic technology, such as high-definition cameras and specialized instruments, continue to enhance the precision and capabilities of endoscopic brain surgery.
-
Postoperative Care:
- Recovery after endoscopic brain surgery is generally faster than with traditional open procedures, but individual recovery experiences may vary.
- Follow-up care and imaging are important to monitor the patient's condition and ensure the success of the surgery.
It's essential to note that not all brain conditions are suitable for endoscopic surgery, and the choice of surgical approach depends on factors such as the type and location of the lesion, the patient's overall health, and the surgeon's expertise. Patients considering endoscopic brain surgery should have a thorough discussion with their medical team to understand the benefits, risks, and potential outcomes specific to their situation.